 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
As a CENTRE FOR RESEARCH IN ALTERNATE SYSTEMS OF ENERGY, the structure essentially needed to serve as a model for the use of energy saving technologies and at the same time demonstrate the potential for the use of alternate energy systems in buildings.The design process has been an exploration in the ways and means to cut energy consumption in the building industry, both in construction as well as maintenance of the building.
The emphasis of the project was on maintaining low energy consumption levels within the centre without compromising on the look and feel of the centre as a premier research organisation. Of the available alternate energy sources, solar energy is most suited to the Indian scenario due to the warm temperate climate and clear skies. Maximum possible use has, therefore been made of this plentiful natural resource. The potential for the use of wind energy is far less at the site as the absence of required wind velocities (above 9 kmph) in Pune, would render the turbines inefficient.
Considerations affecting design
ORIENTATION with respect to sun, wind, etc.
EFFICIENCY in planning, services, etc.
ENERGY SAVING MEASURES
Maximum use of daylight reducing the need for artificial daylighting.
Electronic regulators for fans and use of ballasts in tube lights for
efficient use of energy.
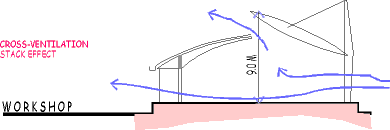
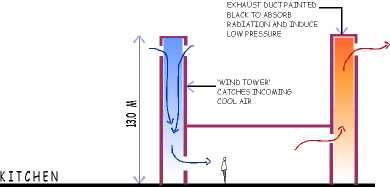
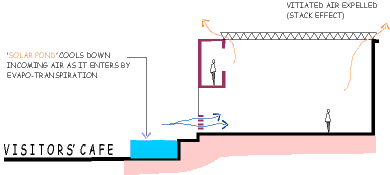
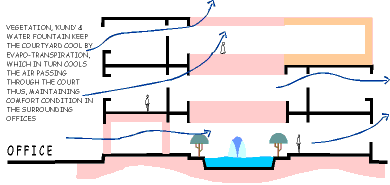
Maintenance of comfort levels by means of effective cross-ventilation,
by the use of courtyards, vegetation and water bodies.
All areas needing air-conditioning grouped together to reduce the service
costs.
All air conditioned-areas insulated with proper shading to reduce cooling
loads. No artificial lighting required during the day, further reducing
cooling loads.
Roof area covered with solar panels wherever possible to reduce heat
gain through the roof and also produce electricity.
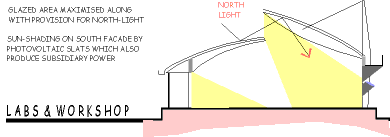
Use of double glazing in laboratory areas to reduce heat gain.
Use of reflective colours and roughcast plaster for shading on south-facing
facades, reducing heat gain.
USE OF ALTERNATE ENERGY SYSTEMS
Solar panels used as roofing material saving the cost of additional
roofing, at the same time producing valuable electricity to supplement
the mains supply.
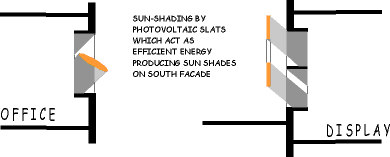
Use of photovoltaic shades on south-facing facades serving the dual
purpose of shading and electricity generation.
Solar pond produces hot water, which can be used to produce electricity
by passing it through a heat exchanger.
Solar collector farm generates hot water, which is used for solar active
space cooling of the library.
Biomass generators used, which saves on conventional fuel like diesel
when necessary biomass feed is available.
Street lighting in the centre accomplished by the use of solar powered
lights. A small biomass plantation with gasifier plant to provide alternate
fuel.